Revolutionising Roadside Brain Injury Assessment using Simulation Software
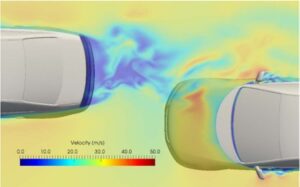
The Oasys LS-DYNA Environments’ software is being used as part of a ground-breaking project led by the Centre for Future Transport and Cities (CFTC) at Coventry University with the aim of saving more pedestrian lives, roadside. CFTC has been awarded a prestigious grant from the Road Safety Trust (£409,319), for the project, “In-Situ Mobile Application for the Triage of Pedestrians in Vehicle Collision (SENTINEL)”.
SENTINEL, which launched in November 2024, is a collaborative three-year project with Coventry University, the University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire NHS Trust, West Midlands Ambulance Service and The Air Ambulance Service, to produce innovative in-situ triage and forensic technology. This project follows CFTC’s Prince Michael International Road Safety Award in 2021 on “Delivering Improved Pedestrian Post Crash Triage”.
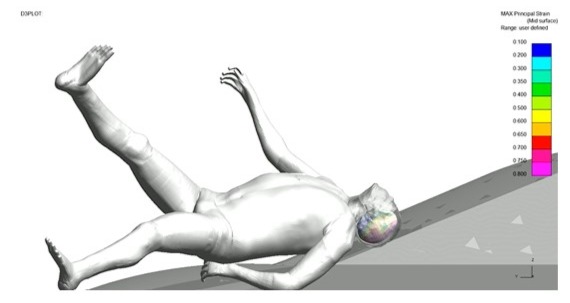
SENTINEL will deliver a validated mobile triage tool that allows prehospital clinicians to assess adult pedestrian brain injuries at the roadside with greater speed, accuracy, and efficiency than current NHS systems. This mobile triage application will be created by performing virtual simulations, using a Toyota Total Human Model for Safety (THUMS) brain computer model, to reconstruct vehicle-to-pedestrian collisions. Pedestrian collisions will be created from the Road Accident in Depth Studies (RAIDS) and reconstructed to generate the training data to create a machine learning model, which can then be converted into a mobile app.
The preparation of brain computation models will be designed using Oasys PRIMER, simplifying the parametrisation and automatic creation of head impact collisions against vehicle structures. SENTINEL will also utilise Oasys T/HIS and Oasys REPORTER to automate brain injury severity outcomes, with the ambition to create a numerical process to perform a virtual “brain injury CT-Scan” using Oasys D3PLOT technology. Researchers in CFTC believe this approach could also allow engineers to assess medical injury outcomes at the design engineering level, leading to the development of safer vehicles.
“This is an ambitious and challenging multi-disciplinary project linking numerical, medical and emergency services experts together with the purpose of saving lives and challenging the status quo on brain injury severity computation. SENTINEL will require the best numerical tools available on the market to improve the project’s productivity and the generation of quality data for the development of our triage mobile app. This research was made possible thanks to the generous funding provided by the Road Safety Trust”
Dr Christophe Bastien, Associate Professor and Principal Investigator. “
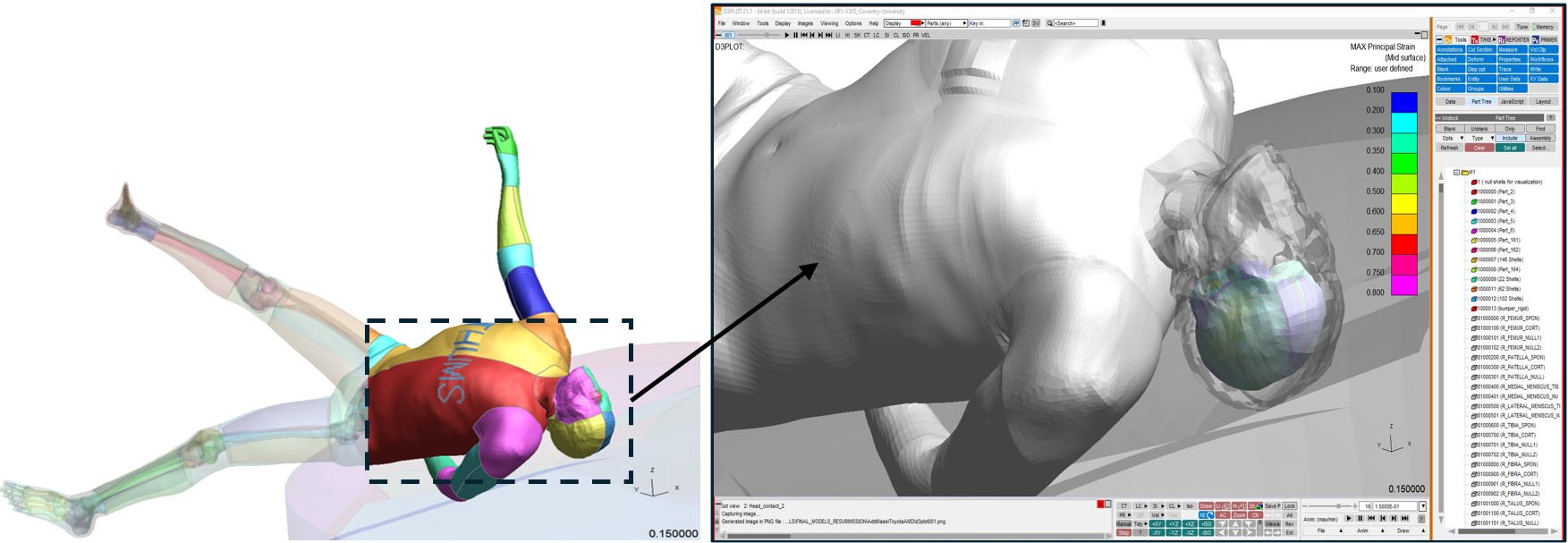
An analysis of pedestrian collisions performed by Coventry University using the Road Accident In-Depth Studies (RAIDS) database has revealed that 8.5% of pedestrian victims with head injury are incorrectly triaged with current clinical assessment of conscious level. This is largely due to the lack of appropriate assessment tools, particularly when victims do not show obvious signs of severe injury at the scene. In 3.8% of pedestrian collision cases, the victims died within 28 days of the incident. Additionally, 4.7% of those who suffered a serious traumatic brain injury experienced lasting physical, cognitive, and psychological effects. The SENTINEL triage tool is designed to help address these challenges.
Project updates can be requested by registering your interest.
Find out more about the project SENTINEL: https://sentinel-rtc.coventry.ac.uk/
Complete the “Expert Insights on Criteria for Estimating Head/Brain Injury Severity in Blunt Trauma” survey: